Sine, Cosine rule

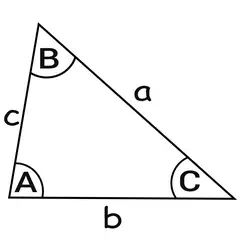
Sine Rule:
The Sine Rule can be used in any triangle (not just right-angled triangles) where a side and its opposite angle are known.
$$ \frac {a}{\sin A} = \frac {b}{\sin B} = \frac {c}{\sin C} $$
Example:
Find the missing side in the diagram below
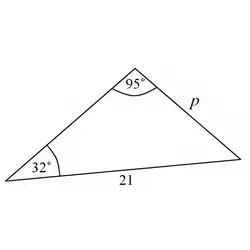
Solution:
$$ \frac {a}{\sin A} = \frac {b}{\sin B} $$
$$ \frac {p}{\sin 32^\circ} = \frac {21}{\sin 95^\circ} $$
$$ p= \frac {21}{\sin 95^\circ} \times \sin 32^\circ $$
$$ p=11.2 $$
Cosine Rule:
The Cosine Rule can be used in any triangle where you are trying to relate all three sides to one angle.
$$ 1. \ a^2 = b^2 + c^2 − 2bc \cos A $$
$$ 2. \ b^2 = a^2 + c^2 − 2ac \cos B $$
$$ 3. \ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 − 2ab \cos C $$
Example 1:
Find Angle "C" Using The Law of Cosines
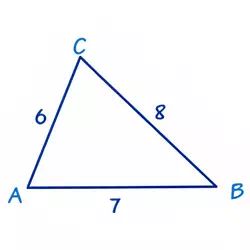
Solution:
In this triangle we know the three sides: a=8, b=6 and c=7
Use The Law of Cosines to find angle C :
$$ \cos C = \frac {(a^2 + b^2 − c^2)}{2ab} $$
$$ \cos C = \frac {(8^2 + 6^2 − 7^2)}{2×8×6} $$
$$ \cos C = \frac {(64 + 36 − 49)}{96} $$
$$ \cos C = \frac {51}{96} $$
$$ \cos C = 0.53125 $$
$$ C = \cos^{−1}(0.53125) $$
$$ C = 57.9^\circ \ \text{to one decimal place} $$
Example 2:
Find the value of x to one decimal place
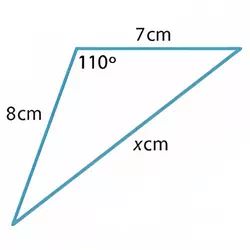
Solution:
Applying the cosine rule gives
$$ x^2=7^2+8^2−2 \times 7 \times 8 \times \cos 110^\circ $$
$$ x^2=113+112 \cos 70^\circ $$
$$ x^2\approx 151.306 $$
$$ x \approx 12.3cm \ (\text{to one decimal place}). $$